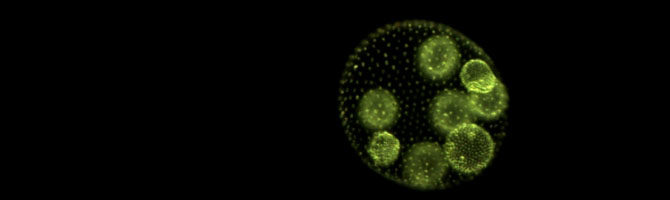
A new paper describing the results of a yeast evolution experiment has been published in Evolution. Jordan Gulli exposed nascent multicellular “snowflake yeast” to an environment in which solitary multicellular clusters experienced low survival. In response, snowflake yeast evolved to form cooperative groups composed of thousands of multicellular clusters.